Demo lesson
This is topic 2 of 18. It’s fully functional and you’re welcome to use it in whatever way you like.
2. Measuring current | I=Q/t
Electricity Explained > Whole class teaching > Charge and current topics
A bit like speed, but not quite the same
2.1 Current as coulombs of charge passing a point each second
2.2 Measuring current by timing charges | Equation I=Q/t
2.3 I=Q/t example calculation
2.4 Conventional current: Imagining all charges are positive and move from positive to negative
2.5 Using an ammeter: Put it in the way of the current you want to measure
2.1 Current as coulombs of charge passing a point each second
Short video summary (2:08)
-
We measure charge by the coulomb (C), not the electron
Faster charges mean a bigger current
Slower charges mean a smaller current
Current is the number of coulombs of charge passing a point each second
-
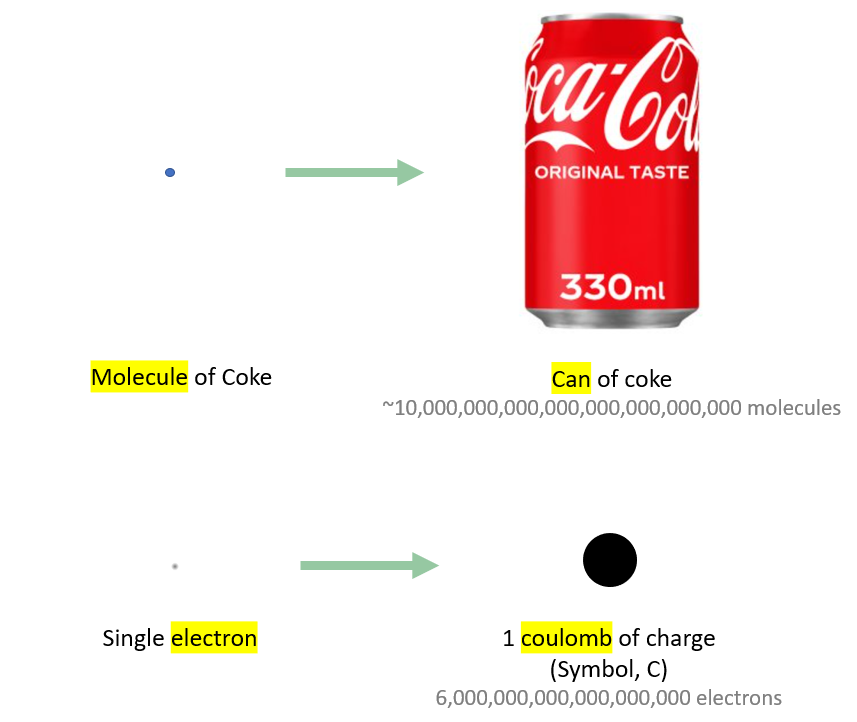
We buy Coca Cola by the can, not the molecule.
For similar reasons, we measure charge by the coulomb (C), not the electron.
To make one coulomb of electric charge we need about 6 billion billion electrons, which is the number of grains of sand on a beach 500 km long.
But electrons and the atoms they come from are so small that there are about ten coulombs of free electrons in every millimetre of copper wire.
In our electric circuit animations we imagine lumping together these billions of free electrons into a single coulomb of charge represented by a black dot.
And it's these single coulombs of electric charge that we imagine moving round the circuit and forming the electric current.
Faster charges mean a bigger current.
Slower charges mean a smaller current.
Even though current is related to the speed the charges move at, it's not exactly the same.
Current is the number of coulombs of charge passing a point each second.
If the same amount of charge passes a point in the same time then by definition the currents are the same.
-
We’ve seen that faster charges mean a bigger current, but we need to introduce the coulomb so that we can define current in amperes properly.
We’re not measuring the speed of charges - what we’re doing is counting the number of coulombs of charge that pass a point each second.
At the moment we’re imagining gathering electrons together to make a coulomb of negative charge, even though the simulations show positive charges and conventional current. We’ll ignore this discrepency until part 2.4 about conventional current.
Even though we talk about the current in the circuit as a whole, when we measure current we really have to specify the point on the circuit we’re talking about.
You imagine standing at that point on the circuit and counting the number of coulombs of charge that pass that point in one second.
It’s an interesting and important idea that charges move quicker through a constriction than they do in the rest of the circuit, though it’s probably too subtle for all but the most able students.
A thin wire has a higher resistance than a thick wire, so swapping a thick wire for a thin one reduces the current everywhere, but the speed of the charges in the thin wire will always be higher than the speed of the charges in the thick wire, even though that might still be slower than the original speed.
It’s because the charges are moving quicker in the thin wire, that that is the part of the circuit where energy is shifted quickest - it’s where the interactions with the lattice happen more frequently.
Key animations from the video for you to use in front of a class
You don’t measure Coke by the molecule
Electrons needed to make a coulomb
10 coulombs of free electrons per mm
Lumping electrons to make a coulomb
Coulombs of charge flowing in a circuit
Same current in different wires
2.2 Measuring current by timing charges | Equation I=Q/t
Short video summary (2:19)
-
The unit of current is the ampere (A)
1 ampere = 1 coulomb per second
We use a capital Q as the symbol for electric charge
We use a capital I for electric current
I=Q/t
The current flowing past a point is equal to the amount of charge flowing past that point divided by the time it took to flow
-
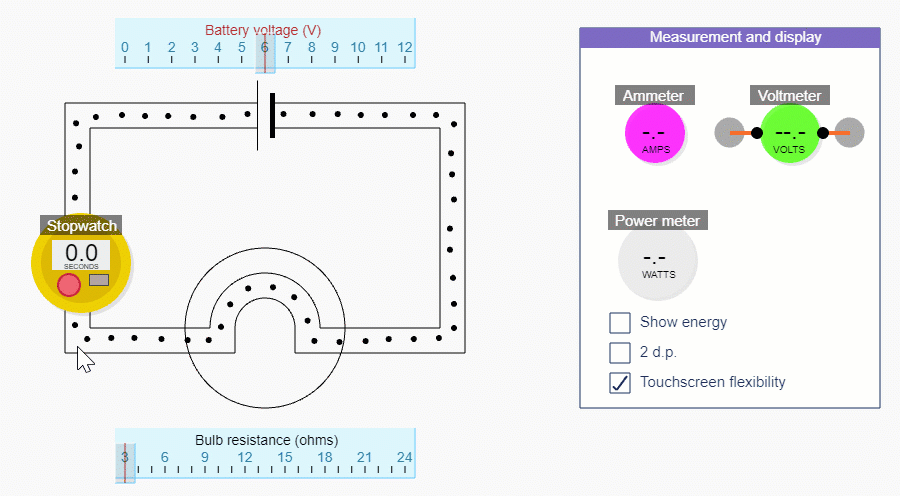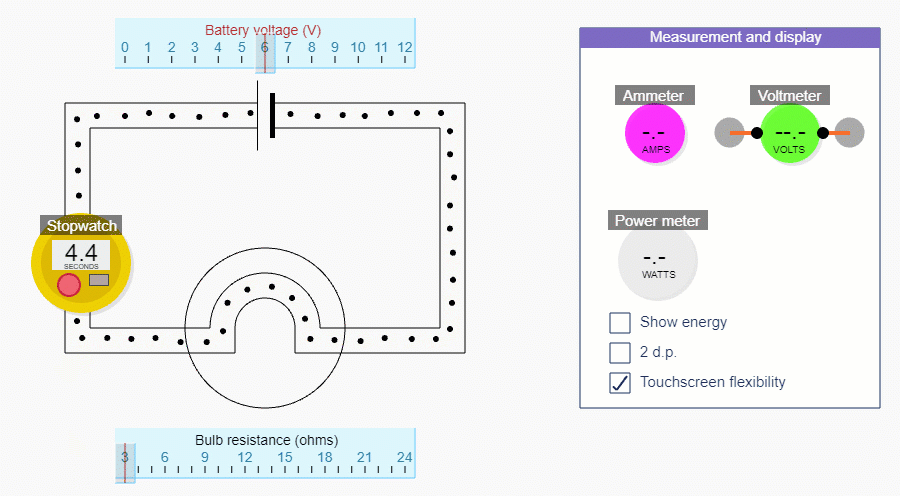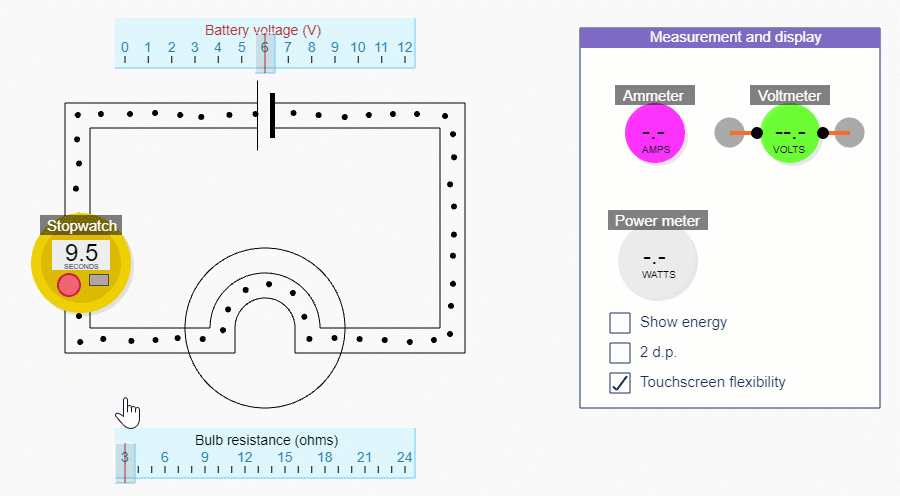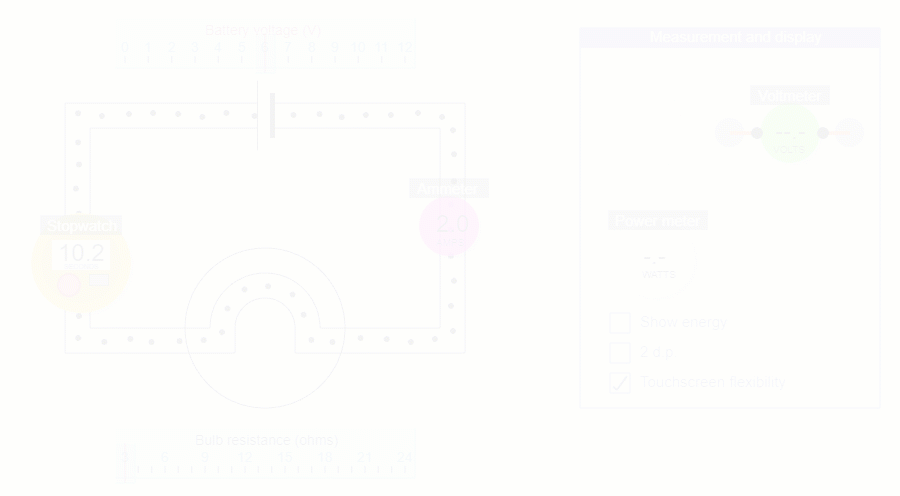
We can calculate current using our simulation by counting the number of charges that pass a point each second.
We'll get a more accurate answer if we count the number of charges that pass a point in, say, 10 seconds and then divide by 10.
The unit of current is the ampere (A)
1 ampere = 1 coulomb per second
1 A = 1 C/s
2 A = 2 C/s, etc
Just like we use the letter m as the symbol for mass and t as the symbol for time, we tend to use a capital Q as the symbol for electric charge (this is because it used to be short for 'quantity of electricity').
We use a capital I for electric current (because André-Marie Ampere used to call it electrical intensity, due to its magnetic effects).
To calculate current we use the equation I=Q/t.
This says the current flowing past a point is equal to the amount of charge flowing past that point divided by the time it took to flow.
-
For this part, it’s better to hide the red stuff in the circuit simulations, by unchecking the Show energy tick box.
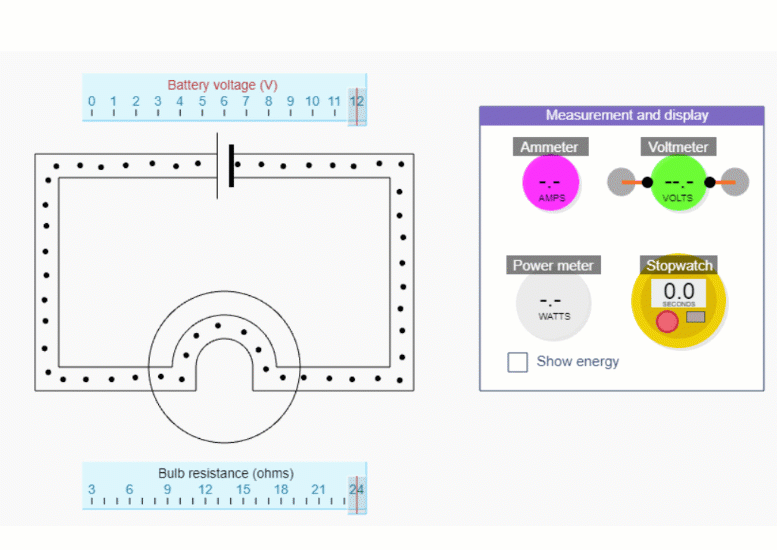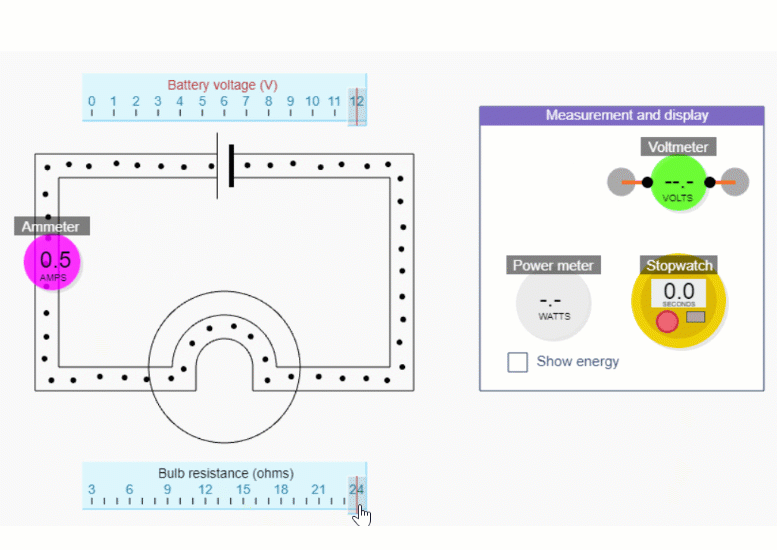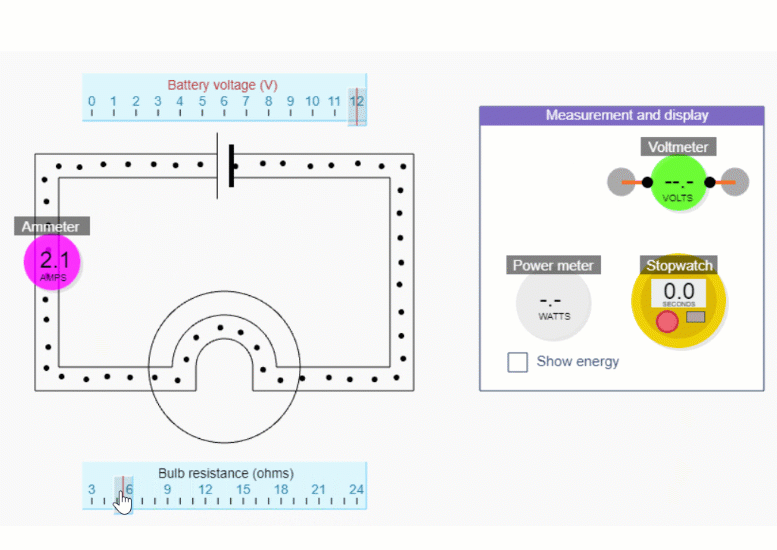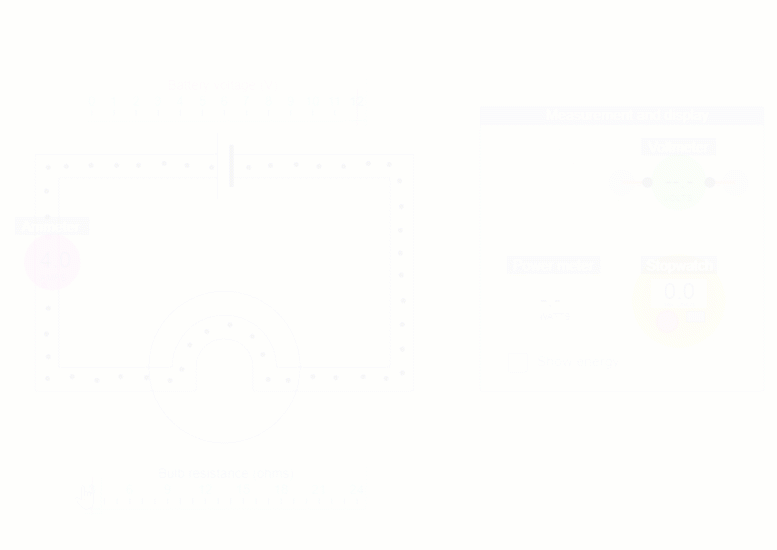
If you reduce the bulb resistance down to 3 ohms, you’ll be able to get the biggest range of currents. Change the current by changing the battery voltage - but remember we’re not trying to show this relationship explicitly.
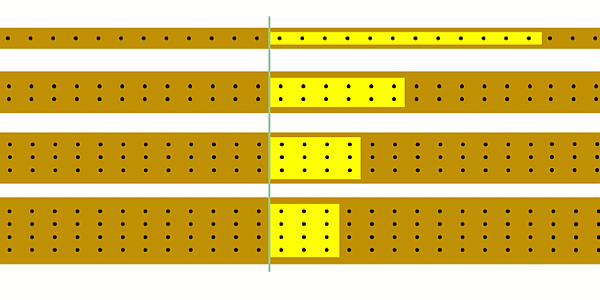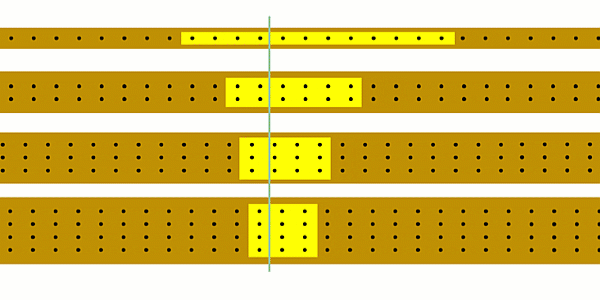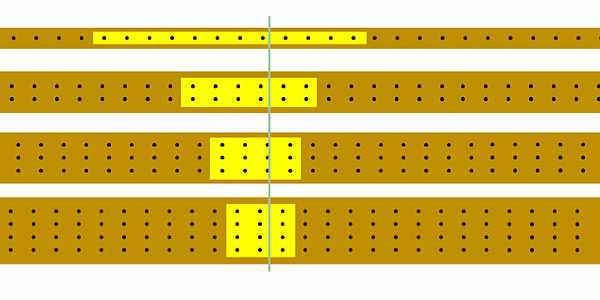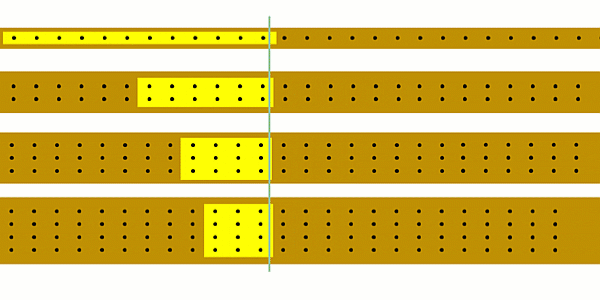
You could start off by using the simulation to show that as you increase the current the number of charges passing a point each second increases.
You could ask students to try and estimate how many charges are passing a point each second.
It’ll become clear that one second is too short a time, so you could see if students realise that you’re better off counting charges for e.g. 10 seconds and then dividing the result by 10.
The simulation is pretty accurate, but it’s not exact, and there is always counting uncertainty, so you may find that a current that should be 1 ampere doesn’t have exactly 10 charges passing a point in 10 seconds - blame the simulation!
Try several calculations for 1 A, 2 A, 3 A, etc. Then try 0.5 A. You could check with the ammeter each time, without going into too much detail about how to use an ammeter - we cover that in Part 5.
How to use the simulation to measure current
Estimating current before using the stopwatch
-
This is a quick qualitative activity where students look at the speed of the charges and try to count/guess how many charges pass a point in 1 second.
You can use the top of the stopwatch as the point you’re measuring the current at.
If you wanted to, you could introduce the ammeter at this point to check students’ answers, and to show that an ammeter effectively counts the number of coulombs of charge that passes through it each second (this isn’t how it actually works!).
Counting the number of charges that pass a point in 10 seconds
-
In this activity you’re actually calculating how many charges pass a point in 1 second by counting the number of charges that pass in 10 seconds (and then dividing by 10!).
It’s much easier to have one person operating the stopwatch and another person counting.
I=Q/t holds whether you count the charges that pass in 10 seconds, or choose a number of charges and time how long they take to pass.
In practice, it’s easier to fix the number of charges to count and then time them.
But intuitively current in amperes is about the ‘amount of charge that passes…’ rather than ‘amount of time it takes…’ so I would stick to fixing the time at 10 seconds.
The other advantage is that the maths is much easier if you wanted to randomly change bulb resistance and battery voltage, and end up with a non-integer value for current that you can check with the ammeter
2.3 I=Q/t example calculation
Short video summary (1:13)
-
How to use the equation I = Q / t to calculate current
-
To calculate current we use the equation I = Q / t.
This says the current flowing past a point is equal to the amount of charge flowing past that point divided by the time it took to flow.
We can use the acronym ESAU to remind us of the four steps we use to solve a numerical problem - Equation, Substitution, Answer, Unit.
-
This is a fairly plain-vanilla piece of physics and is included for completeness.
It’s worthwhile reminding students that t must be measured in seconds.
For more able groups you might want to remind them that the amount of charge moving in a typical laboratory circuit (whether past a point - which is how current is defined - or overall through all the wires) is typically billions of times bigger than for static electricity experiments.
In basic circuits, we may think about hundreds of coulombs of charge moving, but with charging up a balloon we’re talking about a few billionths of a coulomb.
2.4 Conventional current: Positives moving from positive to negative
Short video summary (2:06)
-
It's easier if we pretend that electric currents always consist of positive charges moving in the sense positive to negative
This is called 'conventional current'
It doesn't really matter which way we think they're moving
-
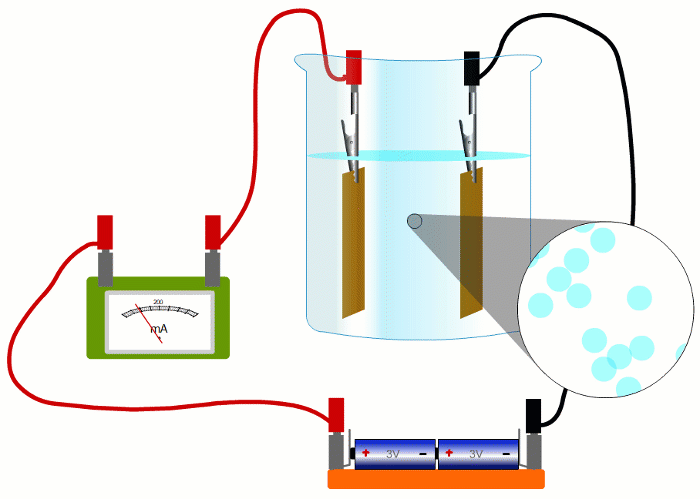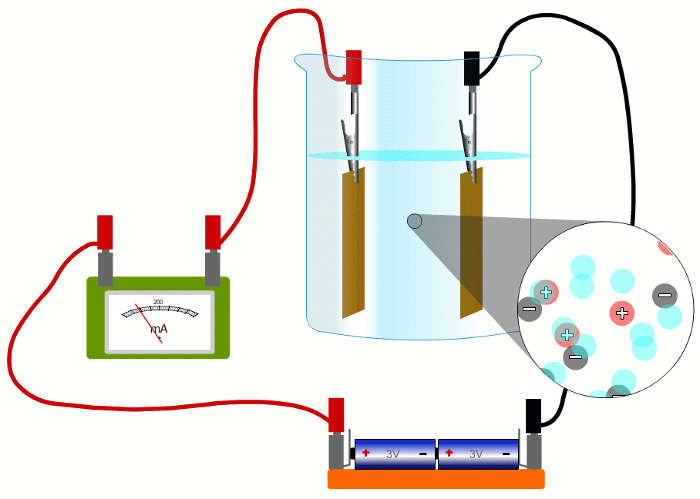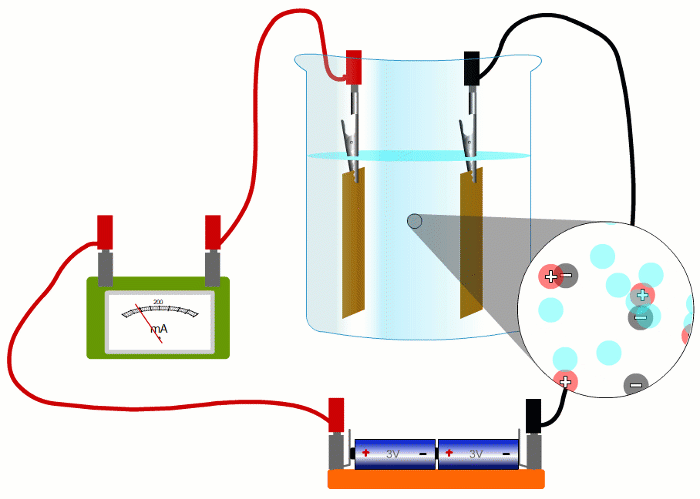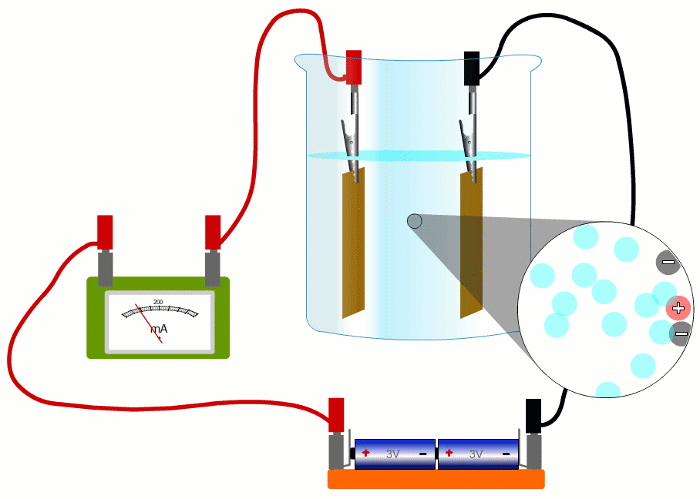
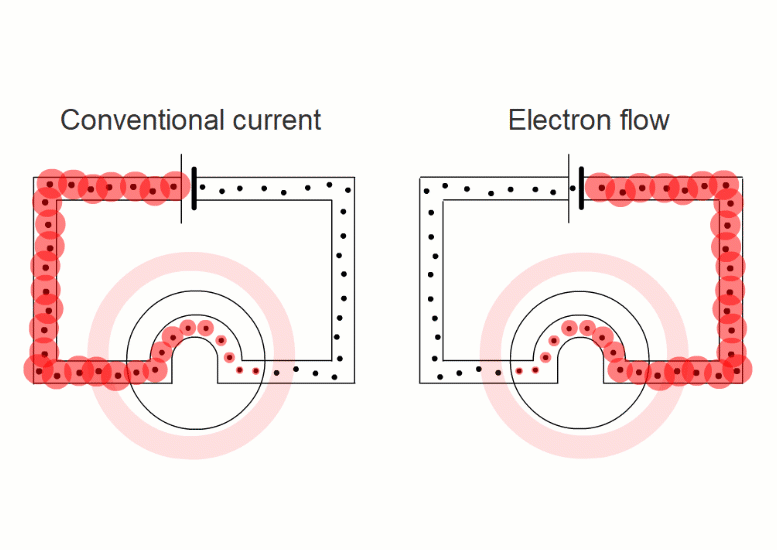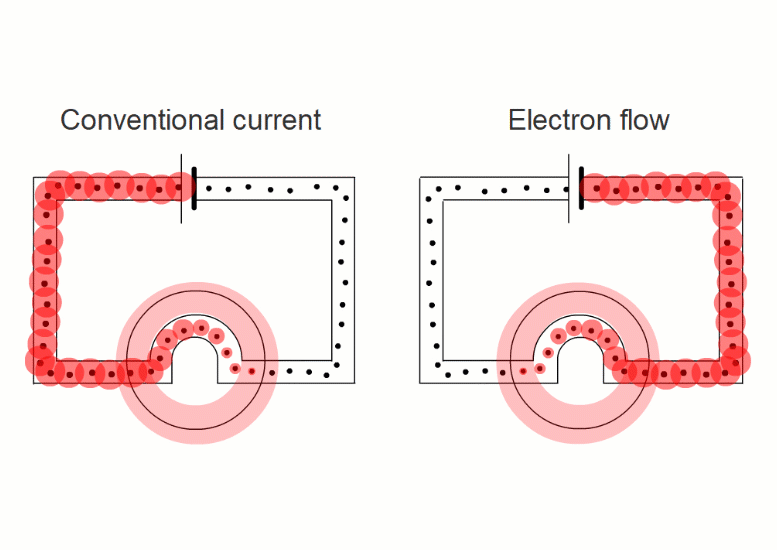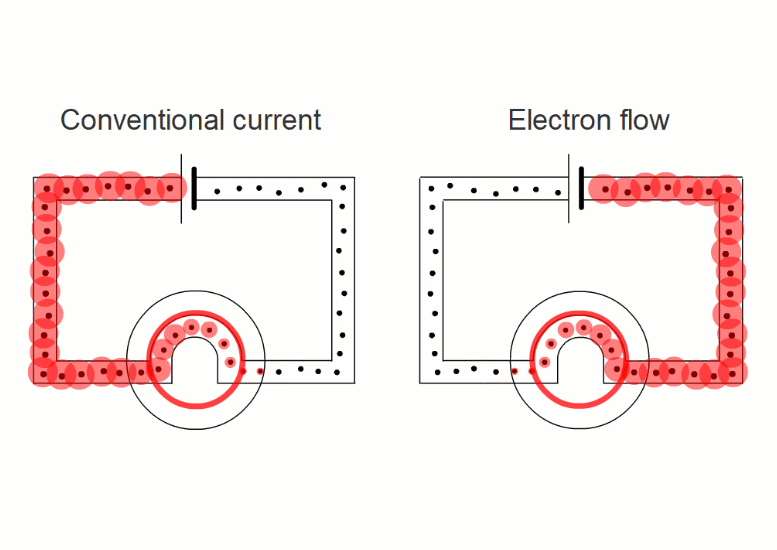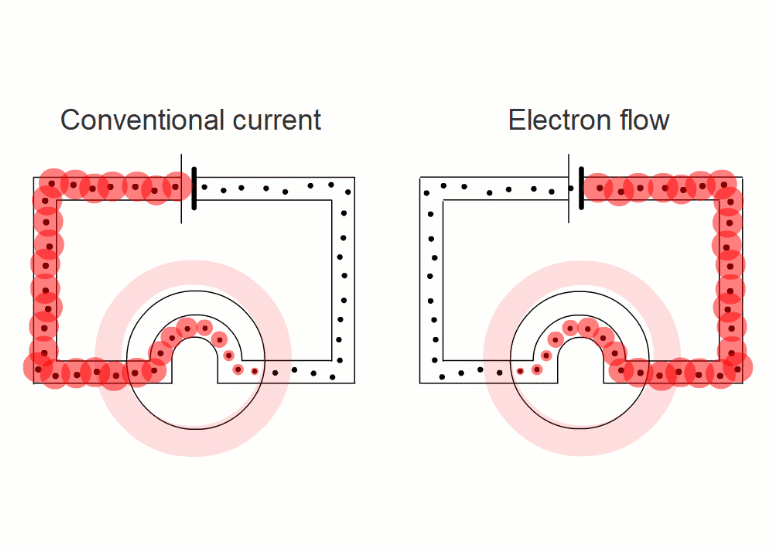
In wires, the charged things that are flowing - the electrons - are negative.
But in liquids they're negative and positive ions moving in opposite directions.
It turns out that it's easier if we pretend that electric currents always consist of positive charges moving in the sense positive to negative.
This is called 'conventional current'.
When negative charges like electrons or negative ions are flowing, we imagine replacing them with positive charges flowing in the opposite direction.
So all our simulations show conventional current, with positive charges moving in the sense positive to negative.
This is how all of science treats electric current, so you end up not having to worry about it.
All the mathematics that ties together electricity and magnetism developed over two hundred years, and assumed that it was positives that were flowing - changing it would mean rewriting millions of pieces of science for no obvious benefit.
In the UK we drive on the left, but in most of the rest of the world people drive on the right.
We could change to driving on the right, but that would be really complicated, expensive and confusing, so we don't.
At least with conventional current everyone in the world 'drives' on the same side.
In electric circuits the charges are already there and they all start moving everywhere at the same time, so it doesn't really matter which way we think they're moving.
-
The typical narrative about conventional current is that ‘scientists made a mistake about electrons’, but this is to over-simplify both the history and the philosophy.
It was in the 1750s that Benjamin Franklin’s experiments with static electricity led him to believe that there were two states of electrically charged objects, which he called positive and negative.
The acceptance of the notion that the world was made up of tiny atoms, and Volta’s invention of the battery didn’t come along until about 1800, so Franklin’s model of what the world was made from, and what experiments he could do were profoundly different from our own.
Franklin’s guess was that there was only one kind of electrical stuff, and that objects were charged when this stuff moved off one and onto another - a good intuition as it turned out. Hence positively charged objects had an excess of electrical stuff and negatively charged objects had a lack.
This is where the ‘mistake’ story comes in. Objects that Franklin thought gained electrical stuff - and hence were positively charged - we now explain by the removal of electrons. So we’ve kept Franklin’s sign convention but reversed the explanation.
Franklin, though, had no sense of innate electrical charge. We now model protons as having an inherent property of being positively charged - they don’t simply lack electrons.
So Franklin was right about charging being (mostly) explicable by the movement of only one substance, but didn’t have our modern view that there are two distinct flavours of charge, not just one.
Key animations from the video for you to use in front of a class
Positive and negative ions in a liquid
Electron flow in a wire
The actual direction makes no difference
Driving on the left would be hard to change
Swapping negative charges for positive
2.5 Using an ammeter: Put it in the way of the current
Short video summary (0:53)
-
To measure current we use an ammeter
Ammeters are connected ‘in series’
-
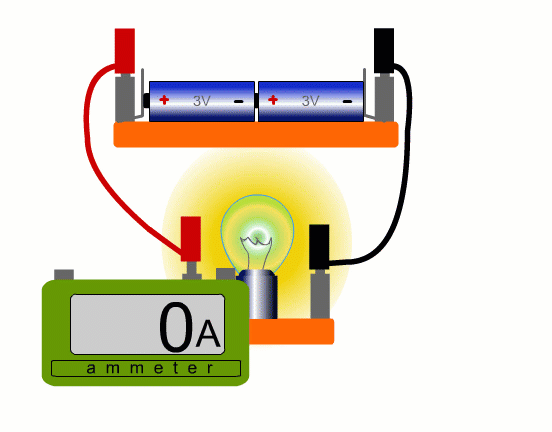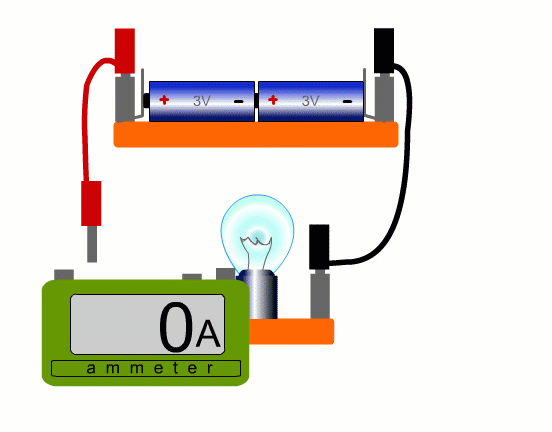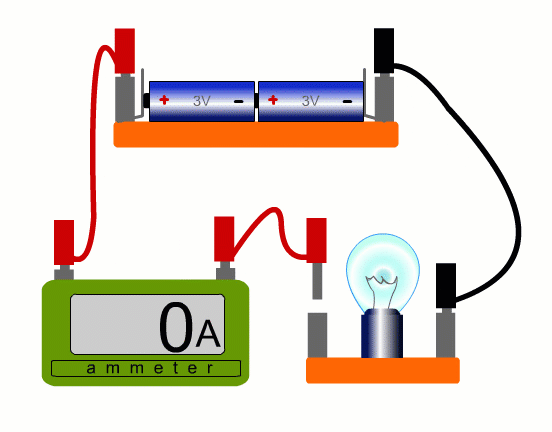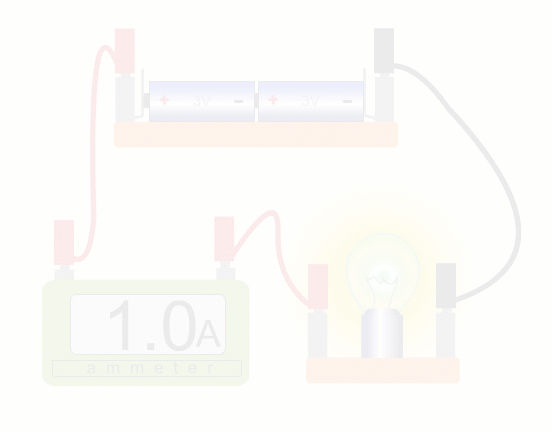
To measure current in a real circuit we use an ammeter.
We need to break the circuit and put the ammeter in the way so that all the current flows through it.
This is called connecting the ammeter 'in series'.
An ammeter is a bit like a speedometer for charges - the faster the charges, the higher the current.
But it's not the speed of the charges that's most important - it's the amount of charge passing a point each second.
-
In our examples we tend to work with integer values for current. This makes the maths easier, but it’s not realistic for the type of circuits we tend to build in the school lab, where currents of about 100 mA are more common.
In our simulation you can put the ammeter anywhere, but with a real circuit, it’s only really practicable to place the ammeter where a lead can easily be removed. You always need an extra lead.
Ammeters have to be hard-wired into a circuit because they are part of the conducting path. Voltmeters are not really part of the circuit, and we can think of them sampling and comparing voltages at two points (though how they work in practice is beyond the scope of these lessons).
Key animations from the video for you to use in front of a class
Breaking the circuit to insert an ammeter
Using an ammeter while increasing current